Often abbreviated as MAP, modified atmosphere packaging is an advanced packing approach geared towards preserving fresh food products. This technique elevates the shelf life of your perishable food products by injecting a unique blend of controlled gases.
Working Principle of Modified Atmosphere Packaging
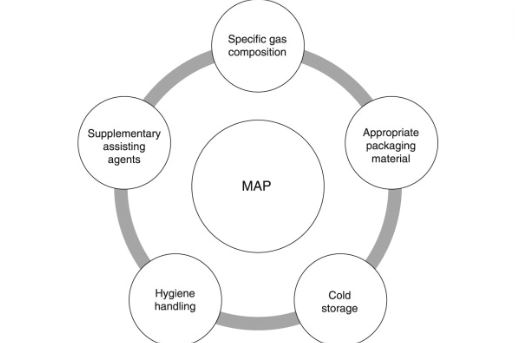
Modified atmosphere packaging is principally designed to decelerate the rate at which your perishable foods spoil.
It accomplishes this by ejecting or shrinking the composition of oxygen in your packaged food before substituting it with a controlled gas mixture. Here is a breakdown of this multi-step process.
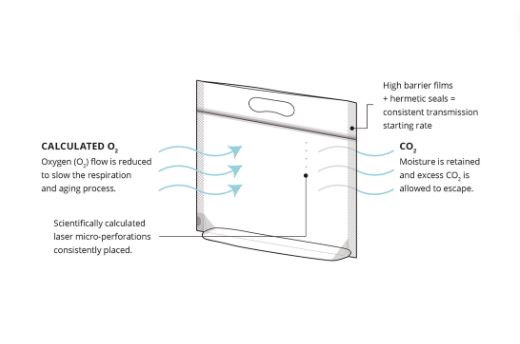
Step 1: Product Selection
The maiden step in MAP requires you to first establish the type of perishable food you are packaging. This helps you determine the ideal gas mixture you will impose on your packaged food to achieve your desired effect.
For instance, imposing a mixture of nitrogen and CO2 into your meat’s packaging will guarantee you a longer shelf life and a natural look.
Step 2: Gas Mixture
Having established the type of food product you are packaging, it is time to choose the right gas combination. Typically, the combination of nitrogen, which is an inert gas with CO2, which is an active gas works well with most foods. With certain foods, oxygen may be necessary especially if you are looking to avert anerobic spoilage.
Step 3: Air Removal
To prepare the packaging for gas imposition, the available gas is first ejected from the packaging. This is often accomplished using several different processes such as;
- Vacuum Flushing: This process sucks out the air present in your packaging consequently leaving it as a near-vacuum environment.
- Purge Flushing: Purge flushing dislodges the unwanted air whilst simultaneously injecting the desired gas combination.
- Displacement Flushing: This process helps you get rid of the unwanted air by injecting higher levels of the controlled gas mixture.
Step 4: Controlled Gas Mixture Flushing
After the unwanted air has been ejected completely or reduced to desirable levels, it is time to impose the controlled gas mixture. The amount of gas injected into your food’s packaging as well as the rate at which it is injected are highly regulated to avert over-gassing. This averts unprecedented food spoilage.
Step 5: Sealing
Once the desired level of controlled gas atmosphere is attained, the packaging is tightly sealed. This helps maintain the perfect gas concentrations thereby guaranteeing a more prolonged shelf life. Some commonly utilized sealing techniques include;
- Mechanical sealing
- Heat sealing
- Vacuum sealing
- Ultrasonic sealing
Step 6: Quality Control
To ensure that the desired food preservation effect is achieved, numerous checks are carried out throughout the modified atmosphere packaging process. For instance, a gas analysis test is undertaken to ensure that the gas composition in your package is perfect.
Techniques Utilized in Modified Atmosphere Packaging
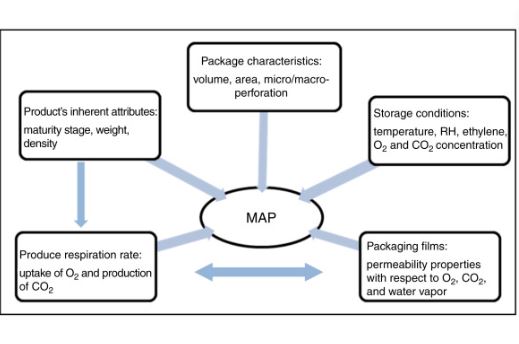
Modified atmosphere packaging simply plays with the air atmosphere in the packaging container storing your food products. To fulfill its purpose, this process utilizes various techniques.
- Gas Flushing: Gas flushing is an elaborate technique that simply flushes out the unwanted air in packaged food before replacing it with a controlled gas blend. This flushing process is often undertaken using varying processes, such as purge flushing and vacuum flushing.
- Passive Modified Atmosphere Packaging: Passive MAP creates a controlled gas atmosphere in your food’s packaging by utilizing natural respiration. This method is often utilized to package and preserve vegetables and fruits. This is because it exploits their ability to absorb oxygen whilst releasing CO2.
- Equilibrium Modified Atmosphere Packaging: This is an advanced technique that amalgamates gas flushing with passive modified atmosphere packaging. This combination helps you achieve the ideal gas composition.
- Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum packaging is a distinct MAP technique that preserves your packaged food by lowering oxygen levels in your package. It creates a near-vacuum atmosphere, making it impossible for microbes to flourish while also mitigating oxidation.
- Skin Packaging: Skin packaging is a packing method that is often merged with MAP to slow down food degradation. It involves the use of a flexible film to wrap your food products after the air has been flushed out.
Modified Atmosphere Packaging Systems
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) systems are elaborate units featuring numerous components that facilitate the proper preservation and packaging of perishable products. These comprehensive machines regulate air concentration and composition while also securely packaging and sealing your food products.
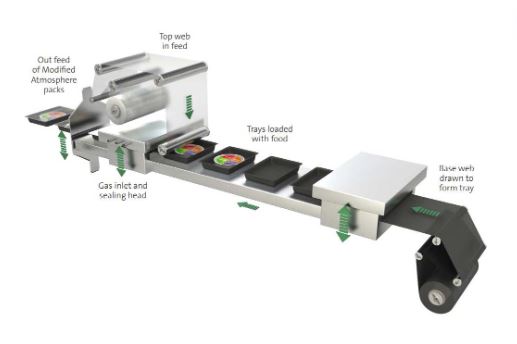
Components of a MAP System
Gas Supply System: The gas supply system comes with a gas tank, regulators, and valves. The gas tanks may be several, with each tank supplying a different type of gas. The valves and regulators determine the rate at which the gas is injected.
Packaging Station: The packaging station is a chamber where your food products are accurately and tightly packaged. It comes with a packaging film, a sealing machine, and a vacuum system.
- Packaging Film: The packaging film places the food products into their respective packaging containers.
- Vacuum System: The vacuum system expels the air present in those packaging containers preserving your perishable food.
Gas Mixing System: These systems also feature gas blenders and analyzers whose roles include blending the varying controlled gases and regulating their composition respectively. The gas analyzers have monitors from where you can observe the gas composition.
Gas Flush System: The featured gas flush system comprises a purge system and nozzles. The gas nozzles are responsible for administering the controlled gas blend into the packaging system. The purge system, on the other hand, is tasked with flushing out residual gases from your packaging.
Control Panel: Contemporary MAP systems come with automated control panels. You get to feed in the desired gas composition as well as the flow rate from the panel. You also get to monitor the performance of your MAP system.
Sensors: To ease the process of quality checking, MAP systems are endowed with varying sensors. These sensors monitor essential parameters like gas flow rate and temperature. They include;
- Temperature sensors
- Pressure sensors
- Gas sensors
Packaging Materials Utilized in Modified Atmosphere Packaging
Modified atmosphere packaging is primarily utilized to package food products with relatively lower shelf lives. The type of material employed to wrap these perishable goods hugely impacts the product’s quality and longevity. Here are some commonly utilized packaging materials;
- Polymeric Film: One of the biggest pros of polymeric film is its resistance to external elements like moisture and even oxygen. In modified atmospheric packaging, this feature is highly appreciated since it retains your perishable products’ quality and freshness.
- Polyethylene: This is a renowned thermoplastic polymer that is revered as a material for wrapping or packing food products. Its prominence in food product packaging is primarily driven by its extreme resistance to pollutants and moisture.
- Polypropylene: Polypropylene films are moderately exploited to package perishable goods due to their flexibility. They are also highly resistant to chemicals, meaning that your packaged food products will remain safe from chemical contaminants.
- Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol: MAP is centered on the lowering of oxygen levels in packaging containers preserving certain food products. EVOH polymer has one of the best oxygen barrier features making it ideal for packaging perishable foods like meat and vegetables.
- Polylactic Acid: Renowned for its eco-friendly status, polylactic acid is gaining immense popularity as a food packaging material. However, there are still challenges impeding its universal acceptance. This includes a relatively lower heat resistance.
- Laminates: Laminates are high-level materials consisting of numerous layers of distinct materials. For instance, some laminates amalgamate polythene and polypropylene and they boast of immense strength.
- Aluminum Foil: The use of aluminum foil as the primary material for modified atmosphere packaging is quite limited. However, whenever it is supplemented with additional layers of other materials like plastic, its prominence grows. It is revered for its ability to keep light, moisture, and oxygen from perishable goods.
- Paperboard: The use of paperboard in MAP is often accompanied by the addition of polymer layers, which elevate its ability to resist external elements. However, it is greatly revered for its printability.
Benefits of Modified Atmosphere Packaging
Perishable products, especially food products are prone to hasty spoilage especially when exposed to oxidation and microbes. To mitigate perishability, innovative packaging techniques such as modified atmosphere packaging have been engineered. MAP in particular comes with a plethora of distinct advantages.
For Consumers
- Fresher Food: MAP preserves your food’s freshness and this translates into longer shelf lives and exquisite tastes.
- Food Safety: Consuming overstayed food or contaminated food products can cause serious health problems. MAP keeps your food fresher for longer while also shielding it from microbial contamination.
- Minimal Wastage: The primary benefit of modified atmosphere packaging is a prolonged shelf life. This translates into reduced product wastage, which has financial and environmental gains.
- Varied Options: Modified atmosphere packaging opens the door for creative packaging, which leaves you with convenient options like packaged, ready-to-eat products.
For Producers, Suppliers and Retailers
- Prolonged Product Lifespan: As a producer or retailer, you want your products to last longer. Packaging perishable goods using modified atmosphere packaging eliminates the conditions and microbes known for causing premature spoilage. This makes certain that your perishable products last longer.
- Savings on Preservatives: Preservatives help prolong product lifespan but they are costly and can alter taste. Utilizing MAP ensures that your goods last longer even without the need for artificial preservatives.
- Longer Distribution Range: As a producer or supplier, you can deliver your perishable goods over long distances without having to worry about premature spoiling. You can also store them over relatively longer periods.
- Better Product Quality: By maintaining the freshness of your food products, modified atmosphere packaging rewards you with high-quality food with an authentic taste and color.
- Reduced Damage Threat: Although the packaging material is not robust, it still offers considerable protection against rough handling.
Comparing Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) to Controlled Atmosphere Packaging (CAP)
Having established that MAP preserves the freshness of perishable goods by regulating the ambient air, it is time to see how it compares to CAP. Controlled atmosphere packaging dwells on the gas composition within a packaging area. This technique ensures that the packaged food is preserved and transported in a controlled atmosphere thereby offering a longer shelf life.
The underlying table illustrates the principal differences between these two prominent packaging methods.
| Features | Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) | Controlled Atmosphere Packaging (CAP) |
| Gas Composition Stability | The gas level keeps changing depending on respiration. | The entire packaging process is highly controlled resulting in a stable gas composition and level. |
| Control Level | Only controls the air composition within the packaging chamber. | Controls the atmosphere within the packaging environment. |
| Shelf Life | Prolong shelf life but not at the same level as CAP. | Prolonged product lifespan for comparatively longer periods. |
| Complexity | Not as complicated as CAP. | Relatively Complicated. |
| Cost | MAP systems are comparatively cheaper. | CAP systems are relatively costlier. |
| Application Scope | Often used to package and preserve fresh produce. | Often used to package and preserve highly perishable goods. |
Modified Atmosphere Packaging Limitations
It is not surprising seeing how modified atmosphere packaging is prominent today. Its multi-faceted rewards have been the primary driving force behind this growth. However, they pack a few shortcomings, which include;
- Limited Applicability: Certain products especially fruits reliant on oxygen tend to lose their freshness and aesthetic appeal when packaged via MAP. Additionally, fatty foods tend to react badly when packaged via MAP.
- Anaerobic Pathogens: The environment created to implement modified atmosphere packaging encourages the growth of anaerobic microorganisms. This poses a contamination risk, which may be challenging to overcome.
Common Applications of Modified Atmosphere Packaging
The ability of MAP to extend the lifespans of perishable goods exceptionally means that it is highly prominent in distinct fields. These fields include;
- Meat Packaging: MAP keeps raw meat raw for considerably longer days compared to conventional packaging.
- Fruits Packaging: In fruit processing and packaging, MAP is broadly utilized to preserve the freshness and tastiness of fruits such as apples.
- Vegetable Packaging: It is also prominently exploited to package vegetables while preserving their leafy look and feel.
- Seafood Packaging: Modified atmosphere packaging is revered in seafood packaging since it conserves the rawness of seafood.
- Mushroom Packaging: MAP is universally exploited to package mushrooms because it keeps them firm and prevents the eruption of their caps.
- Processed Meat Packaging: It is prominently utilized to package sausages and other processed meat products because it retains their color.
- Ready-to-eat-meals Packaging: MAP conserves the tastiness and freshness of ready-to-eat snacks like sandwiches and chips.
- Bakery Products Packaging: In bakeries, MAP has been widely adopted since it prolongs the freshness timeline of bread and other bakery products.
- Coffee Beans: Modified atmosphere packaging inhibits oxidation and this helps preserve the aroma and tastiness of coffee beans.
- Cut Flowers: MAP comes in handy when packaging cut flowers since it retains their freshness and beauty.
- Fresh Herbs Packaging: Modified atmosphere packaging is the preferred option for packaging basil, cilantro, and other herbs.
At JOCHAMP, we offer safe and effective packaging solutions for the most demanding food packaging industry.
More Resources:
Frozen Food Packaging – Source: JOCHAMP
Food Packaging Line – Source: JOCHAMP
Modified Atmosphere – Source: WIKIPEDIA


